Embark on a historical journey with the Pieces Chart AP World History, a tool that unlocks the complexities of global events. Delve into its origins, structure, and applications, and discover how this chart empowers historians and students alike to unravel the tapestry of world history.
The Pieces Chart AP World History provides a comprehensive framework for analyzing historical events, interactions, and trends. Its unique structure and elements offer a deeper understanding of global history, enabling us to identify patterns, draw comparisons, and make connections across different eras.
Historical Context

The Pieces of Eight chart is a crucial tool in AP World History, providing a comprehensive timeline of significant global events from 1450 to the present day. Its origins can be traced back to the 1990s, when a group of educators recognized the need for a resource that would help students understand the interconnectedness of world history.
The chart was developed by a team led by Dr. Peter Stearns, a renowned historian and author. The team’s goal was to create a resource that would help students identify key themes, patterns, and connections in global history. The chart has since become an essential resource for students, teachers, and scholars alike.
Use of the Chart
The Pieces of Eight chart has been widely used to analyze and understand global history. It has been employed in classrooms, research projects, and academic publications. The chart has helped scholars identify trends, make comparisons, and draw connections between different regions and time periods.
Chart Structure and Elements
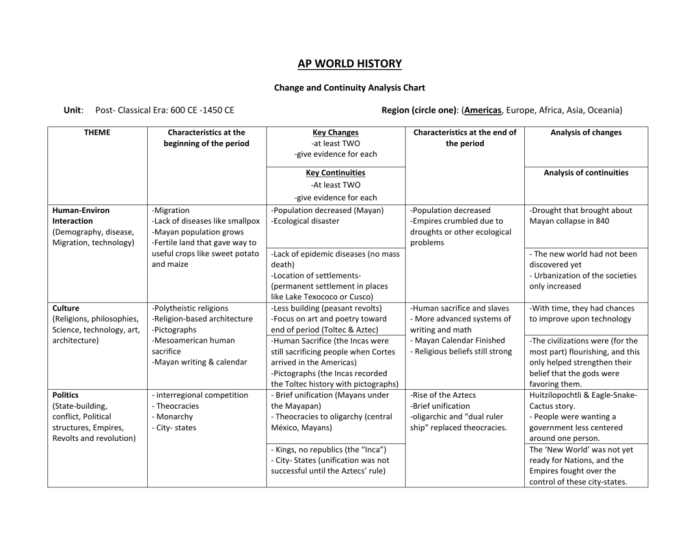
The Pieces of Eight chart is a comprehensive tool for analyzing world history, providing a structured framework for understanding the complex interactions and developments that have shaped our world.
The chart is organized into three main sections: Context, Content, and Consequences. Each section is further divided into specific categories that explore different aspects of historical events and trends.
Context
The Context section provides essential background information about the historical period being studied. It includes categories such as geography, demographics, technology, and culture, which help establish the setting and conditions that influenced historical events.
Content
The Content section focuses on the specific events, developments, and processes that occurred during the historical period. It includes categories such as politics, economics, religion, and social change, which examine the key drivers and outcomes of historical events.
Consequences
The Consequences section explores the long-term effects and outcomes of historical events. It includes categories such as legacy, impact, and lessons learned, which provide insights into how past events have shaped the present and offer valuable lessons for the future.
Key Elements and Variables
The Pieces of Eight chart also includes a number of key elements and variables that help to identify and analyze historical trends. These include:
- Chronology:The chart is organized chronologically, allowing for the identification of patterns and changes over time.
- Causation:The chart examines the causes and effects of historical events, helping to establish relationships and identify key factors that influenced outcomes.
- Comparison:The chart facilitates the comparison of different historical periods and regions, highlighting similarities and differences in historical experiences.
- Interpretation:The chart provides a framework for interpreting historical events and drawing conclusions about the past.
Applications in AP World History
The Pieces of Eight chart is a valuable tool for analyzing historical events and processes in AP World History. It provides a framework for understanding the complex interactions between different societies and cultures.
Pieces charts are a great way to organize information for AP World History. They can help you see the big picture and make connections between different events and ideas. If you’re looking for a comprehensive study guide for the EIPA written test, I recommend checking out this resource: eipa written test study guide . It covers everything you need to know for the exam, including how to use pieces charts effectively.
By using pieces charts and studying effectively, you’ll be well on your way to success on the AP World History exam.
By examining the eight categories of the chart, students can gain insights into the causes and consequences of global interactions, cultural diffusion, and the rise and fall of civilizations.
Analyzing Specific Historical Events
The Pieces of Eight chart can be used to analyze specific historical events, such as the Columbian Exchange or the Industrial Revolution. By examining the different categories of the chart, students can identify the key factors that contributed to these events and their impact on the world.
Understanding Global Interactions
The chart also helps students understand how different societies and cultures interacted with each other. For example, by examining the “Trade and Technology” category, students can see how the development of new technologies, such as the compass and the printing press, facilitated global trade and cultural exchange.
Identifying Patterns and Making Connections
The Pieces of Eight chart can also be used to identify patterns and make connections across different historical periods. For example, by comparing the “Political Structures” category in different civilizations, students can see how different forms of government have evolved over time.
Limitations and Criticisms
The Pieces of Eight chart, while a valuable tool for historical analysis, has certain limitations and criticisms that users should be aware of.One limitation is that the chart is based on a Eurocentric perspective, meaning it focuses primarily on events and developments in Europe and its colonies.
This can lead to a biased or incomplete understanding of world history, as it overlooks or minimizes the contributions and experiences of non-European societies.Another criticism is that the chart’s coverage of certain time periods and regions is uneven. For example, the chart devotes more space to the early modern period and the West than to other periods and regions.
This can create the impression that these areas and time periods are more important or significant than others.
Addressing Limitations, Pieces chart ap world history
These limitations can be addressed by using the chart in conjunction with other sources and perspectives. For example, users can consult non-Western histories or primary sources to gain a more balanced understanding of world history. Additionally, users can be mindful of the chart’s Eurocentric bias and make an effort to seek out information from a variety of perspectives.By
being aware of the chart’s limitations and taking steps to address them, users can use the Pieces of Eight chart as a valuable tool for understanding the complexity and diversity of world history.
Alternative Perspectives
While the Pieces of Eight chart offers a valuable framework for analyzing global history, it is important to recognize that it is not the only perspective. Alternative charts, frameworks, and approaches can complement or challenge the chart’s interpretations, providing a more comprehensive understanding of world history.
Big History Timeline
The Big History Timeline, developed by David Christian, presents a comprehensive narrative of the universe’s history from the Big Bang to the present. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of all things and challenges the traditional division of history into ancient, medieval, and modern periods.
The timeline encourages a broader perspective on human history within the context of the vastness of time and space.
World Systems Theory
World Systems Theory, proposed by Immanuel Wallerstein, analyzes the global economy as a hierarchical system of core, periphery, and semi-periphery regions. It argues that the economic exploitation of the periphery by the core drives global inequality and development. World Systems Theory provides an alternative lens for understanding the rise and fall of empires and the impact of colonialism on global history.
Environmental History
Environmental History focuses on the relationship between humans and the natural world. It examines how environmental factors have shaped human societies and how human activities have impacted the environment. Environmental History challenges the traditional emphasis on political and economic factors in history, highlighting the importance of the natural world in shaping human development.
Comparative History
Comparative History involves comparing different societies and civilizations across time and space. It seeks to identify similarities and differences in their development and to draw generalizable conclusions about human behavior and social organization. Comparative History can challenge assumptions about the uniqueness of particular historical experiences and provide insights into the commonalities of human experience.
Transnational History
Transnational History examines the movement of people, ideas, and goods across national borders. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of different parts of the world and challenges the traditional focus on nation-states as the primary units of historical analysis. Transnational History provides a more nuanced understanding of globalization and its impact on human history.
FAQ Insights: Pieces Chart Ap World History
What is the Pieces Chart AP World History?
The Pieces Chart AP World History is a visual representation of global history, divided into eight sections that analyze different aspects of historical events and processes.
How can I use the Pieces Chart AP World History in my studies?
The Pieces Chart AP World History can be used to identify patterns, draw comparisons, and make connections across different historical periods, helping students understand global interactions and the rise and fall of civilizations.
Are there any limitations to the Pieces Chart AP World History?
While the Pieces Chart AP World History is a valuable tool, it is important to acknowledge its potential biases or gaps in coverage. It is essential to consider alternative perspectives and methodologies to gain a more comprehensive understanding of world history.