Unveiling the intricacies of consumer behavior, the Price Elasticity of Demand Worksheet emerges as an indispensable tool. This guide delves into the concept, calculation, and application of elasticity, empowering businesses with insights to optimize pricing strategies and maximize revenue.
Through real-world examples and practical exercises, this worksheet unravels the factors influencing elasticity, its limitations, and advanced concepts like cross-price and income elasticity. Prepare to gain a comprehensive understanding of consumer demand and make informed pricing decisions that drive business success.
Understanding Price Elasticity of Demand
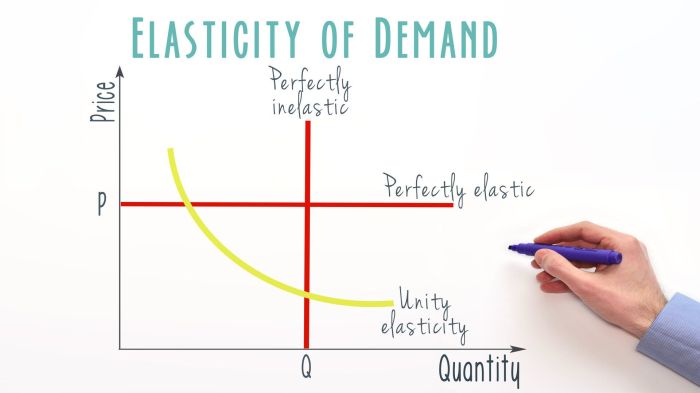
Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
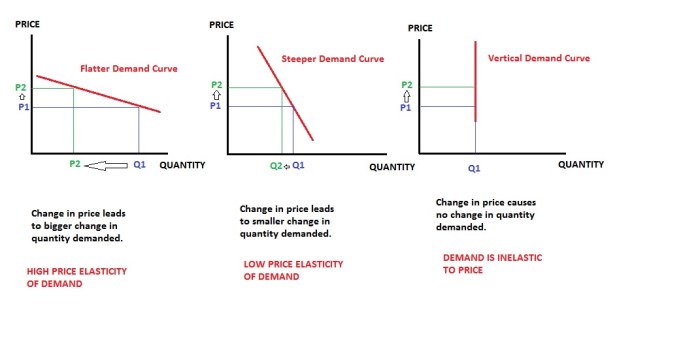
Demand can be either elastic or inelastic. Elastic demand means that a small change in price will lead to a large change in quantity demanded. Inelastic demand means that a small change in price will lead to a small change in quantity demanded.
Real-World Examples
- Elastic demand:Gasoline. When the price of gasoline goes up, people tend to drive less.
- Inelastic demand:Insulin. When the price of insulin goes up, people with diabetes still need to buy it.
Calculating Price Elasticity of Demand
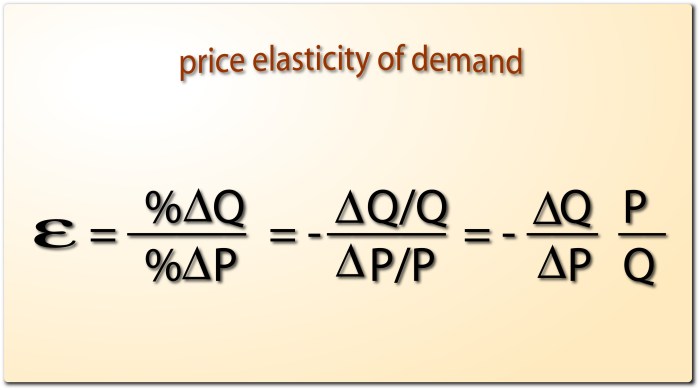
Calculating the price elasticity of demand involves using a formula that measures the percentage change in quantity demanded relative to the percentage change in price. Understanding this formula is crucial for determining the responsiveness of consumers to price changes.
Formula for Calculating Price Elasticity of Demand
The formula for calculating price elasticity of demand is as follows:
Price Elasticity of Demand = (% Change in Quantity Demanded) / (% Change in Price)
Where:
- % Change in Quantity Demanded = ((New Quantity Demanded – Old Quantity Demanded) / Old Quantity Demanded) – 100
- % Change in Price = ((New Price – Old Price) / Old Price) – 100
Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand
Price elasticity of demand is a measure of how responsive the quantity demanded of a good or service is to changes in its price. Several factors influence the elasticity of demand, including:
Availability of Substitutes
- If close substitutes are readily available, consumers are more likely to switch to alternatives when the price of a particular good or service increases, resulting in higher elasticity.
- Example: If the price of Coca-Cola increases, consumers may switch to Pepsi, leading to a more elastic demand for Coca-Cola.
Importance of the Good
- Goods that are considered essential or important in daily life tend to have lower elasticity of demand.
- Example: The demand for gasoline is relatively inelastic because it is essential for transportation.
Proportion of Income Spent on the Good
- If a good represents a significant portion of consumers’ income, changes in its price will have a greater impact on their purchasing decisions, leading to higher elasticity.
- Example: The demand for luxury goods is typically more elastic than the demand for basic necessities.
Time Horizon
- In the short run, consumers may be less responsive to price changes, resulting in lower elasticity.
- In the long run, consumers have more time to adjust their consumption patterns, leading to higher elasticity.
Using Price Elasticity of Demand in Decision-Making
Understanding price elasticity of demand is crucial for businesses to make informed pricing decisions. By considering the responsiveness of demand to price changes, businesses can optimize their pricing strategies to maximize revenue and profitability.
Pricing Decisions
Price elasticity provides insights into the impact of price changes on demand. Businesses can use this information to:
- Set optimal prices: Elasticity helps determine the price point that maximizes revenue. By considering the demand curve and elasticity, businesses can identify the price that balances demand and profitability.
- Predict revenue changes: Understanding elasticity allows businesses to forecast the impact of price changes on revenue. This enables them to make informed decisions about price adjustments, promotions, and discounts.
Maximizing Revenue
Price elasticity can be used to maximize revenue in several ways:
- For inelastic demand (elasticity< 1), increasing price leads to increased revenue. This is because the reduction in quantity demanded is outweighed by the higher price per unit.
- For elastic demand (elasticity > 1), decreasing price leads to increased revenue. This is because the increase in quantity demanded more than compensates for the lower price per unit.
By understanding price elasticity, businesses can make strategic pricing decisions that optimize revenue and achieve their business goals.
Limitations of Price Elasticity of Demand
Price elasticity of demand is a useful tool for understanding how consumers respond to price changes, but it has certain limitations and assumptions that must be considered when using it.
One limitation is that price elasticity of demand assumes that all other factors affecting demand remain constant. In reality, factors such as income, tastes, and preferences can also influence demand, and changes in these factors can affect the accuracy of elasticity estimates.
Time Horizon
Another limitation is that price elasticity of demand can vary over time. In the short run, consumers may be less responsive to price changes than in the long run, as they may need time to adjust their consumption habits.
Product Availability
The availability of substitutes and complements can also affect price elasticity of demand. If there are many close substitutes available, consumers may be more likely to switch to a different product if the price of one product increases, resulting in a higher elasticity of demand.
Consumer Behavior, Price elasticity of demand worksheet
Finally, price elasticity of demand assumes that consumers are rational and make decisions based on economic factors. However, consumer behavior is often influenced by psychological and emotional factors, which can make it difficult to predict how they will respond to price changes.
Advanced Concepts: Price Elasticity Of Demand Worksheet
Beyond the basic concept of price elasticity of demand, more advanced concepts offer deeper insights into consumer behavior. These include cross-price elasticity and income elasticity.
Cross-Price Elasticity
Cross-price elasticity measures the responsiveness of demand for one product to changes in the price of another product. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded for one product divided by the percentage change in price of the other product.
A positive cross-price elasticity indicates that the products are substitutes, while a negative cross-price elasticity indicates that they are complements.
Income Elasticity
Income elasticity measures the responsiveness of demand for a product to changes in consumer income. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity demanded for a product divided by the percentage change in consumer income. A positive income elasticity indicates that the product is a normal good, while a negative income elasticity indicates that it is an inferior good.
These advanced concepts provide a more comprehensive understanding of consumer behavior by considering the effects of price changes on related products and consumer income.
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of price elasticity of demand?
Price elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of consumer demand to price changes, providing valuable insights into consumer behavior and market dynamics.
How can businesses use the Price Elasticity of Demand Worksheet?
The worksheet guides businesses in calculating elasticity, identifying factors that influence it, and leveraging this knowledge to optimize pricing strategies and maximize revenue.
What are the limitations of using price elasticity of demand?
While elasticity provides valuable insights, it has limitations, such as the assumption of constant other factors and the potential for consumer behavior to change over time.