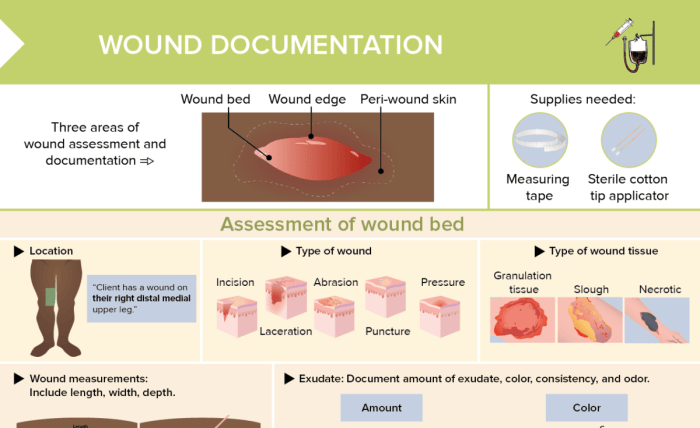
A nurse is documenting data about a deep necrotic wound, a critical step in managing and treating the wound effectively. Deep necrotic tissue poses significant challenges, and accurate documentation is essential for ensuring proper care and preventing complications. This article provides a comprehensive overview of a nurse’s role in assessing, documenting, and managing deep necrotic wounds.
Understanding the characteristics, causes, and potential complications of deep necrotic tissue is crucial for nurses. Accurate wound assessment, including size, location, depth, and drainage, is essential for developing an effective treatment plan. Infection management is also a critical aspect of wound care, and nurses play a vital role in identifying signs and symptoms of infection and implementing appropriate interventions.
Deep Necrotic Tissue Assessment
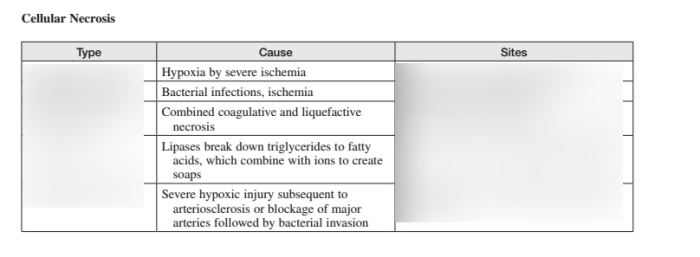
Deep necrotic tissue is characterized by its black or brown discoloration, firm texture, and foul odor. It can occur in various body locations, including pressure sores, diabetic ulcers, and surgical wounds.
Necrosis is the death of tissue due to lack of blood supply. It can be caused by a number of factors, including trauma, infection, and chronic diseases such as diabetes.
Wound Assessment
| Characteristic | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Size | Measured in centimeters (cm) |
| Location | Anatomical description of wound site |
| Depth | Classified as superficial, partial-thickness, or full-thickness |
| Drainage | Characterized by amount, color, and consistency |
Wound assessment tools include rulers, wound probes, and swabs. Accurate documentation is essential for tracking wound progress and evaluating the effectiveness of treatment.
Infection Management
Signs and symptoms of wound infection include redness, swelling, pain, and drainage. Wound infection can be prevented by proper wound care, including regular cleansing and dressing changes.
Wound cleansing should be performed with sterile saline or an antiseptic solution. Dressings should be changed as needed to keep the wound clean and dry.
Patient Education
Patient education is crucial for wound care and prevention. Patients should be instructed on how to monitor their wounds for signs of infection, how to perform wound care, and how to avoid activities that may damage the wound.
A patient education handout should include information on wound care techniques, signs and symptoms of infection, and the importance of patient involvement in wound management.
Documentation and Reporting, A nurse is documenting data about a deep necrotic
Nursing notes should document the characteristics of the deep necrotic tissue, including its color, texture, and odor. The location, size, and depth of the wound should also be documented.
Legal and ethical considerations related to wound documentation include the patient’s right to privacy and the nurse’s responsibility to provide accurate and timely documentation.
Clear and concise reporting is essential for effective communication between healthcare providers and for ensuring that the patient receives appropriate care.
Essential FAQs: A Nurse Is Documenting Data About A Deep Necrotic
What are the key characteristics of deep necrotic tissue?
Deep necrotic tissue is characterized by its black or brown color, firm texture, and foul odor.
What are the potential causes of deep necrosis?
Deep necrosis can be caused by various factors, including pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, and severe burns.
What are the signs and symptoms of wound infection?
Signs and symptoms of wound infection include redness, swelling, pain, drainage, and fever.