What’s the greenhouse effect weegy? It is a natural process that plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s temperature. This article delves into the intricacies of the greenhouse effect, exploring its mechanisms, impacts, and the role of human activities in its enhancement.
The greenhouse effect is a complex phenomenon with far-reaching implications. Understanding its nuances is essential for addressing climate change and ensuring a sustainable future.
Define the Greenhouse Effect
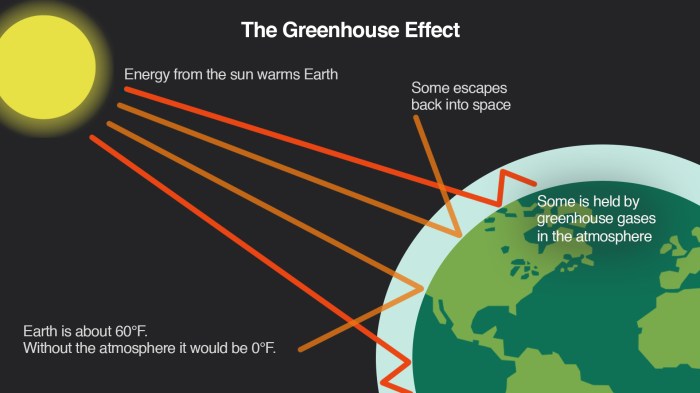
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that occurs when certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat radiated from the planet’s surface. These gases, known as greenhouse gases (GHGs), allow sunlight to pass through the atmosphere but absorb and emit heat back toward the Earth.
The primary greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, but human activities have significantly increased their concentrations, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming.
Explain the process of the greenhouse effect, What’s the greenhouse effect weegy
The greenhouse effect can be visualized as a greenhouse made of glass or plastic. Sunlight passes through the glass and warms the objects inside the greenhouse. The objects then emit heat in the form of infrared radiation, which is trapped by the glass and cannot escape, causing the greenhouse to become warmer.
In the Earth’s atmosphere, GHGs act similarly to the glass in a greenhouse. Sunlight passes through the atmosphere and warms the Earth’s surface. The Earth’s surface then emits heat in the form of infrared radiation, which is absorbed and re-emitted by GHGs, trapping heat in the atmosphere and causing the planet to warm.
Provide examples of greenhouse gases
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): Emitted from burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
- Methane (CH4): Released from landfills, livestock farming, and natural gas production.
- Nitrous oxide (N2O): Produced by agricultural activities, industrial processes, and burning fossil fuels.
- Fluorinated gases (F-gases): Synthetic gases used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and industrial processes.
Impacts of the Greenhouse Effect
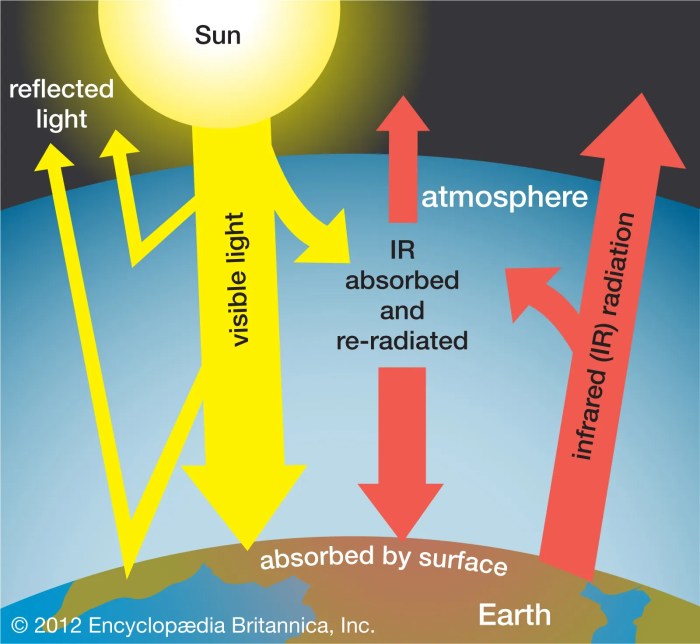
The enhanced greenhouse effect caused by increased GHG concentrations has significant consequences for the Earth’s climate and ecosystems.
Discuss the consequences of increased greenhouse gas concentrations
- Rising global temperatures: Increased GHG concentrations trap more heat in the atmosphere, leading to an overall increase in global temperatures.
- More frequent and intense extreme weather events: Climate change caused by the greenhouse effect exacerbates extreme weather events such as heatwaves, droughts, floods, and storms.
- Sea level rise: As global temperatures rise, ocean waters expand and glaciers melt, contributing to sea level rise and threatening coastal communities.
- Ocean acidification: Increased CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere dissolve into the ocean, making it more acidic and harming marine life.
Share data on global temperature changes
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the global average surface temperature has increased by approximately 1.1°C (2°F) since the pre-industrial era (1850-1900).
Projections indicate that global temperatures will continue to rise in the coming decades, with the potential for significant impacts on human societies and ecosystems.
Human Contributions to the Greenhouse Effect
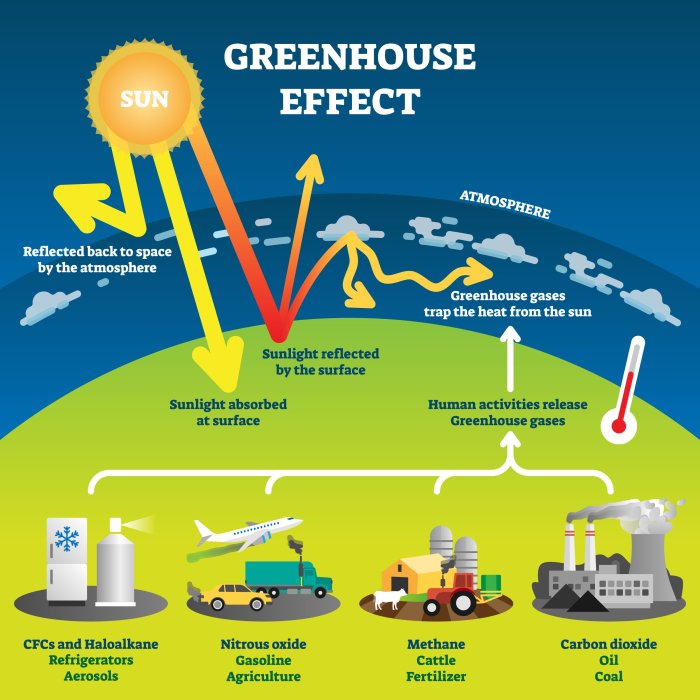
Human activities are the primary driver of the enhanced greenhouse effect. The burning of fossil fuels for energy production, transportation, and industrial processes releases large amounts of GHGs into the atmosphere.
Explain the role of human activities in greenhouse gas emissions
- Energy production: Burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas releases CO2 and other GHGs.
- Transportation: Vehicles powered by gasoline and diesel emit CO2 and other GHGs.
- Industrial processes: Manufacturing, mining, and other industrial activities release GHGs such as CO2, CH4, and N2O.
- Agriculture: Livestock farming, rice cultivation, and fertilizer use contribute to CH4 and N2O emissions.
Provide examples of industries and practices that contribute to emissions
- Coal-fired power plants
- Oil refineries
- Natural gas extraction and transportation
- Automobile and aircraft manufacturing
- Livestock farming (particularly cattle and sheep)
- Rice cultivation
- Industrial processes such as cement production and steel manufacturing
Mitigating the Greenhouse Effect
Addressing the greenhouse effect requires a concerted effort to reduce GHG emissions. This can be achieved through a combination of technological, policy, and behavioral changes.
Describe potential solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
- Transition to renewable energy sources: Replacing fossil fuels with renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower reduces CO2 emissions.
- Energy efficiency measures: Improving the efficiency of energy use in buildings, transportation, and industry reduces the demand for energy and GHG emissions.
- Carbon capture and storage (CCS): Technologies that capture CO2 from industrial processes or the atmosphere and store it underground can help reduce emissions.
- Reforestation and afforestation: Planting and restoring forests helps absorb CO2 from the atmosphere.
Share examples of renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures
- Solar panels
- Wind turbines
- Hydroelectric power plants
- Geothermal energy
- Energy-efficient appliances
- LED lighting
- Improved insulation in buildings
- Efficient public transportation systems
Quick FAQs: What’s The Greenhouse Effect Weegy
What are greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that absorb and emit radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process traps heat in the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect.
What are the primary sources of greenhouse gas emissions?
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels for energy and transportation, deforestation, and industrial processes, are the primary sources of greenhouse gas emissions.
What are the potential consequences of the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect leads to global temperature rise, which can result in sea-level rise, extreme weather events, changes in precipitation patterns, and disruptions to ecosystems.