Discover the best cement for zirconia crowns and embark on a journey to enhance the longevity and aesthetics of your dental restorations. With a wide range of options available, selecting the optimal cement is crucial for ensuring a strong bond, preventing complications, and achieving exceptional results.
Factors such as crown type,咬合力, and desired aesthetics play a vital role in cement selection. This guide delves into the intricacies of zirconia crown cementation, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions for optimal oral health.
Types of Cement for Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns, known for their strength and aesthetics, require specific types of cement to ensure a strong and durable bond between the crown and the underlying tooth structure. Different types of cement offer unique advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand their properties before selecting the most suitable option for each individual case.
Resin Cements, Best cement for zirconia crowns
Resin cements are a popular choice for zirconia crowns due to their high bond strength and versatility. They are composed of a resin matrix and a filler material, providing a strong and durable bond to both zirconia and tooth structure.
Resin cements are available in various shades, allowing for a natural-looking restoration that blends seamlessly with the surrounding teeth.
- Advantages:High bond strength, versatility, aesthetic results
- Disadvantages:May require additional bonding agents, potential for polymerization shrinkage
Glass Ionomer Cements
Glass ionomer cements (GICs) are another option for cementing zirconia crowns. They are composed of a glass powder and a polyacrylic acid liquid, which react to form a strong and chemically bonded interface with both zirconia and tooth structure. GICs release fluoride ions, which contribute to the prevention of secondary caries around the crown margins.
- Advantages:Chemical bonding, fluoride release, biocompatibility
- Disadvantages:Lower bond strength compared to resin cements, may be more brittle
Zinc Phosphate Cements
Zinc phosphate cements are traditional cements that have been used for many years in dentistry. They are composed of zinc oxide powder and a phosphoric acid liquid, which react to form a hard and durable cement. Zinc phosphate cements are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, but they have a lower bond strength compared to resin cements.
- Advantages:Inexpensive, easy to use
- Disadvantages:Lower bond strength, may be more acidic
Factors to Consider When Choosing Cement
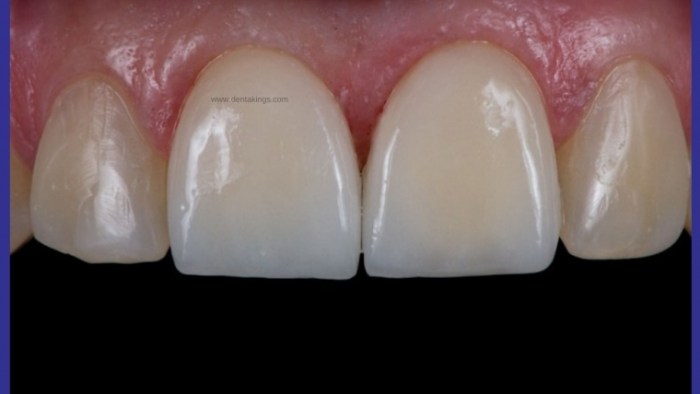
Selecting the optimal cement for zirconia crowns is crucial for the restoration’s success. Several factors should be carefully considered to ensure the cement’s compatibility with zirconia and the longevity of the restoration.
These factors include:
Bond Strength
- The bond strength between the cement and zirconia surface is paramount for the restoration’s stability and resistance to dislodgement.
- Cements with high bond strength provide a secure and durable connection between the crown and the prepared tooth structure.
Marginal Adaptation
- The cement’s ability to achieve a precise and tight fit at the crown margins is essential for preventing microleakage and bacterial infiltration.
- Proper marginal adaptation ensures the longevity of the restoration and reduces the risk of secondary caries.
Film Thickness
- The thickness of the cement film between the crown and the tooth should be minimal to maintain the strength of the restoration.
- Excessive film thickness can compromise the bond strength and increase the risk of fracture.
Biocompatibility
- The cement should be biocompatible with the oral tissues, causing no adverse reactions or inflammation.
- Non-toxic and hypoallergenic cements ensure the patient’s safety and comfort.
Radiopacity
- The cement’s radiopacity allows for easy visualization on dental radiographs, facilitating the diagnosis of any potential problems.
- Radiopaque cements aid in the detection of excess cement or voids, ensuring proper restoration assessment.
Application Techniques
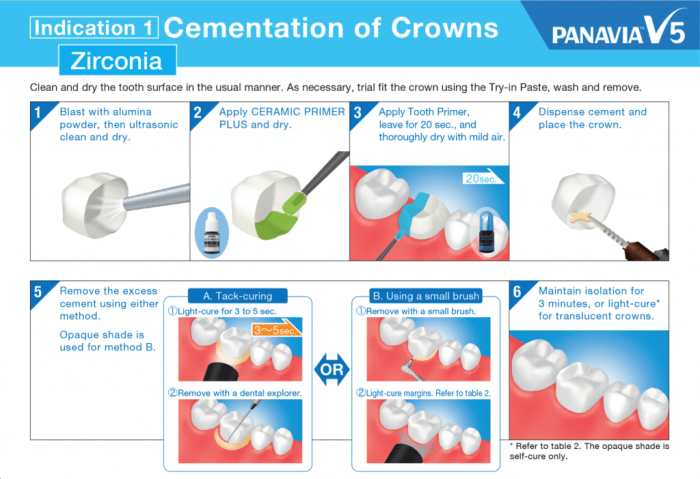
Proper application of cement is crucial for achieving a strong and durable bond between the zirconia crown and the prepared tooth structure. The following step-by-step guide provides a comprehensive overview of the application process:
Step 1: Preparation– Clean and dry the prepared tooth and the inner surface of the zirconia crown thoroughly. – Apply a thin layer of primer to the tooth surface and allow it to dry according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Step 2: Cement Selection– Select a cement that is specifically designed for zirconia crowns and is compatible with the type of zirconia used. – Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing the cement to the correct consistency.
Step 3: Cement Application– Apply a thin layer of cement to the inner surface of the crown. – Position the crown on the prepared tooth and gently seat it into place. – Use firm, even pressure to ensure complete seating.
Step 4: Excess Cement Removal– Remove any excess cement that squeezes out from around the margins of the crown using a cotton pellet or a scaler. – Be careful not to damage the cement bond.
Step 5: Curing– Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for curing the cement. This may involve light curing, chemical curing, or a combination of both. – Ensure complete curing to achieve the desired bond strength.
Tips and Tricks:– Use a microbrush or a small brush to apply the cement evenly. – Apply the cement in a thin layer to avoid creating voids or excess bulk. – Use a glycerin gel to prevent the cement from sticking to the instruments.
– Hold the crown in place for the recommended curing time to ensure a secure bond. – Protect the bond from moisture during the curing process.
Long-Term Performance
Long-term performance of cement for zirconia crowns is crucial for the longevity and success of the restoration. Different cement types exhibit varying degrees of durability and stability over time.
Several studies have evaluated the long-term performance of different cements. A 5-year clinical study by Guess et al. (2012) found that resin-modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) and self-adhesive resin cement (SARC) showed comparable clinical success rates for zirconia crowns. Both cements maintained high bond strength and marginal integrity over the study period.
Another study by Kern and Wegner (2014) compared the long-term performance of conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and RMGIC for zirconia crowns. After 10 years of clinical service, RMGIC exhibited significantly higher bond strength and less marginal deterioration compared to GIC.
This suggests that RMGIC may provide superior long-term durability for zirconia crowns.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
When cementing zirconia crowns, various issues may arise. Understanding these problems and implementing effective solutions can enhance the longevity and aesthetics of the restoration.
To prevent these problems, meticulous attention to detail during the preparation, selection of cement, and cementation procedure is paramount. By adhering to proper protocols and utilizing appropriate techniques, dentists can minimize the likelihood of complications and ensure optimal outcomes.
When selecting the best cement for zirconia crowns, it’s crucial to consider the surrounding environment. Just as abiotic factors like temperature and salinity impact the health of coral reefs coral reefs 1 abiotic factors , the choice of cement should complement the oral environment to ensure optimal crown performance and longevity.
Cement Dislodgement
- Inadequate surface preparation: Ensure thorough cleaning and etching of both the crown and tooth surfaces to create a strong bond.
- Insufficient cement thickness: Use an appropriate amount of cement to fill the space between the crown and tooth, ensuring complete seating and preventing gaps.
- Improper curing: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for curing the cement to achieve optimal strength and bond.
Marginal Discoloration
- Excess cement: Remove any excess cement promptly to prevent staining or discoloration along the margins.
- Inadequate isolation: Protect the margins from moisture contamination during cementation to prevent discoloration.
- Cement choice: Opt for cements with low water solubility and minimal color change over time.
Sensitivity
- Excessive cement pressure: Avoid applying excessive pressure during cementation, as it can cause discomfort or sensitivity.
- Improper isolation: Ensure adequate isolation to prevent leakage of cement into the pulp chamber.
- Cement choice: Consider using cements with low acidity to minimize pulp irritation.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies demonstrate the successful application of zirconia crowns with various cement types. These studies provide valuable insights into the long-term performance and effectiveness of different cementation techniques.
Case Study: Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cement
A study conducted at the University of California, Los Angeles, evaluated the long-term performance of zirconia crowns cemented with resin-modified glass ionomer cement. After five years, the crowns exhibited excellent retention and marginal integrity, with no signs of fracture or debonding.
The cement provided a strong bond to both the zirconia and the tooth structure, ensuring the longevity of the restoration.
Future Developments
The field of cement technology for zirconia crowns is constantly evolving, with researchers exploring innovative materials and techniques to enhance the performance and longevity of restorations.
One promising area of research involves the development of self-adhesive cements that eliminate the need for a separate bonding agent. These cements simplify the application process, reduce the risk of errors, and may provide a stronger bond between the crown and the tooth structure.
Advanced Materials
Researchers are also investigating the use of advanced materials, such as nanomaterials and bioactive glasses, to improve the properties of zirconia cements. These materials have the potential to enhance bond strength, reduce microleakage, and promote osseointegration, ultimately leading to more durable and biocompatible restorations.
Expert Answers: Best Cement For Zirconia Crowns
What is the strongest cement for zirconia crowns?
Resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) cements are generally considered the strongest cements for zirconia crowns due to their high bond strength and durability.
How long does zirconia crown cement last?
With proper care and maintenance, zirconia crown cement can last for many years. Factors such as咬合力, oral hygiene, and the type of cement used can influence its longevity.
Can zirconia crowns be recemented?
Yes, zirconia crowns can be recemented if they become loose or dislodged. The process involves removing the old cement, cleaning the surfaces, and applying new cement to reattach the crown.